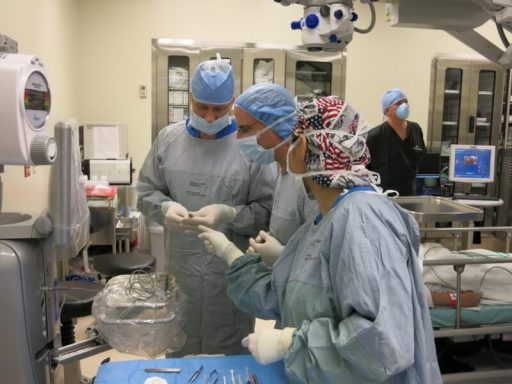
Normally, the pupil reacts actively to variable lighting conditions. In good lighting, it is narrow, becoming wider in the evening and at night. Some pharmacological substances cause the pupil to expand, facilitating examination of the eye or eye surgery. In a significant number of patients, due to co-morbidities or the use of medications, insufficient pupil expansion (mydriasis) is present. This problem greatly complicates cataract removal, and is often accompanied by several other negative factors (weakness of the lens zonules, blood-ocular barrier disruption, increased risk or ocular inflammation, etc.).
- Glaucoma.
- Pseudoexfoliation syndrome.
- Previous eye inflammation (uveitis, iridocyclitis, eye surgery, etc.).
- Age-related atrophy of the iris.
- Intake of medications (for the treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia, systemic hypertension, psychosis, etc.).
- Diabetes.
Small pupil is not a “dead-end” for cataract removal. The modern ophthalmologist has a number of effective methods for addressing this challenge. At the same time, it is important to understand that cataract surgery in the case of small pupil is associated with the risks of lens capsule rupture, iris trauma, vitreous loss, and significant inflammation.

You can make an appointment by phone from 8:30 to 19:30 (daily).
A small, poorly dilated pupil simply cannot provide enough space for the surgeon to work. Access to the lens is very limited and the surgeon’s effectiveness is greatly constrained. To avoid undesirable consequences during and after the surgical procedure, a number of special technological advances have been developed.
The surgical armamentarium includes use of special phaco machine settings, use of proper viscoelastic with a higher viscosity, dissection of the adhesions between the lens and pupil, and other techniques. In relatively mild cases, intraocular injection of a mydriatic drug turns out to be very useful and quite sufficient. In other cases, a gentle stretching of the pupil with microsurgical instruments is needed. Most frequently, mechanical and pharmacological methods are combined.
The Malyugin ring is a pupil-expander device popular among surgeons across the world.
- Vision is decreased by 50% or more.
- Unwanted optical phenomena and decreased contrast sensitivity are causing discomfort and interfere with regular activities at home or at work.
- Changes in visual perception are decreasing quality of life.
- The patient sees halos around light sources.
- The disease has reached an advanced stage.
Ophthalmic surgeons share experiences and new methods for conducting complicated surgery at international congresses yearly. Science does not stand still; surgical procedures are becoming safer and more effective. New methods and surgical tools are continually being developed and appearing in the doctor’s toolkit, aimed at providing immediate assistance in difficult cases.